|
Industry Standards
The industry standards for Wireless LAN include several variations of 802.11 and HiperLAN. The 802.11 standards include the original 802.11, 802.11a, 802.11b, and 802.11g versions. These standards primarily vary based on frequency bands and data transmission rates. The 802.11 series of industry standards are based on 802.3 Ethernet technologies. This allows the WLAN system to more easily integrate with existing wired Ethernet systems. The 802 family of standards include 802.1 (management), 802.2 (link layer control), and 802.3 (Ethernet technology).
Prior to 802.11 industry standardization, there were many wireless LAN (WLAN) systems in use worldwide and many of these systems use radio communications protocols that are proprietary to the manufacturer of WLAN equipment. This has resulted in incompatibility between products. To overcome this limitation, the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) created an industry standard specification in June 1997 (802.11) that defines a wireless protocol for homogeneous systems. The IEEE 802.11 standard for wireless LANs (WLANs) allows interoperability among products from different vendors.
The 802.11 specifications have three transmission options; one infrared (IR) option and two radio frequency (RF) options: direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) and frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS).
When choosing a wireless LAN system, customers should consider their future requirements and how the system can be expanded or changed to meet the needs of their future requirements. An Infrared (IR) system provides a basic 1 Mbps data transfer rate with an option for a 2 Mbps system. The Radio Frequency systems can provide data transfer rates from 1 Mbps to 54 Mbps. -30-
802.11 The original 802.11 standard offered WLAN on a frequency band of 2.4 GHz with data transfer rates of 1 or 2 Mbps. The original 802.11 systems could use frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS) or direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS) radio transmission. Optionally, this system could use Infrared (IR) transmission instead of radio transmission.
802.11A 802.11a is a high-speed data version of the 802.11 wireless local area network (WLAN) industry standard. It was developed to operate in the 5.7 GHz spectrum and permits data transmission speeds up to 54 Mbps. The 802.11a system provides for 8 non-overlapping 25 MHz wide channels and up to 64 users per access point (AP).
Figure_WALN_16 shows the frequency band and radio channel size that is used in the 802.11a system. This example shows that the basic radio channel in the 802.11a system is 25 MHz wide and that the center frequency of the radio channel can be assigned to different points (channels) in the three 100 MHz wide 5.7 GHz industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) unlicensed frequency bands.
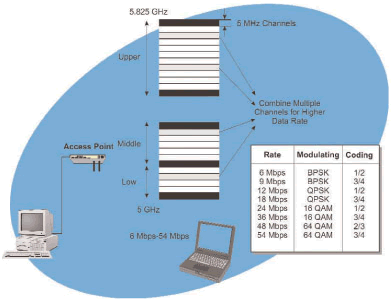
Figure_WALN_16: 802.11a Radio
802.11B 802.11b operates in the 2.4 GHz frequency band and has a data transfer rate up to 11 Mbps. 802.11B systems are backward compatible to the original 802.11 system. 802.11b provides for 3 non-overlapping channels and up to 32 users per access point (AP).
Figure_WALN_17 shows the frequency band and radio channel size that is used in the 802.11b system. This example shows that the basic radio channel in the 802.11b system is 25 MHz wide and that the center frequency of the radio channel can be assigned to different points (channels) in the 83 MHz industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) unlicensed frequency band. This example shows that there can be up to 3 non-interfering (non-overlapping) 802.11b radio channels operating in the same ISM frequency band.
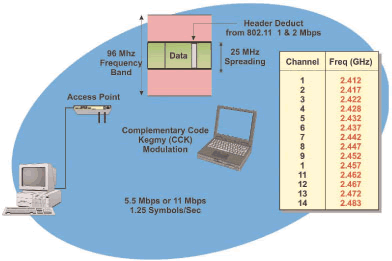
Figure_WALN_17: 802.11b Radio
802.11G 802.11g are a Wireless LAN standard that operates in the 2.4 GHz bands that provides up to 54 Mbps of data transmission speed. 802.11G are backward compatible to 802.11B. 802.11g provides for 3 non-overlapping channels.
Figure_WALN_16 shows the different product groups of 802.11 systems and how the data transmission rates have increased in the 802.11 WLAN over time as new more advanced modulation technologies are used. The first systems could only transmit at 1 Mbps. The current evolution of 802.11A and 802.11G allows for data transmission rates of up to 54 Mbps.
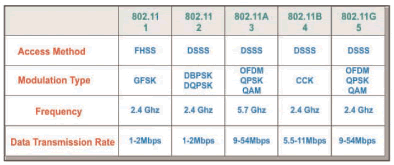
Figure_WALN_18: Wireless LAN System Types
HyperLAN HyperLAN is a wireless local area network (WLAN) specification overseen by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). It operates in the 5.7 GHz industrial, scientific, and medical (ISM) frequency band. HyperLAN provides for data transmission rates of up to 54 Mbps. HyperLAN also uses the 802.3 Ethernet standard for its' fundamental structure.
|

